
After this come a pair of ill-defined areas called the presubiculum and parasubiculum, then a After CA1 comes an area called the subiculum.

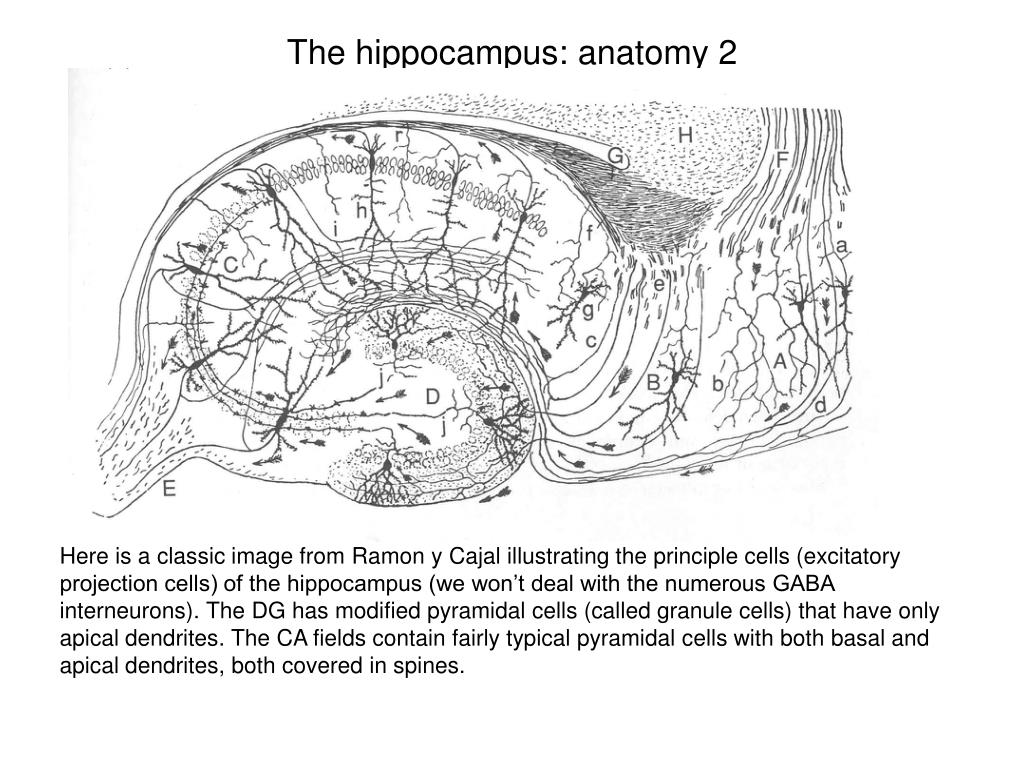
The CA areas are all filled with densely packed pyramidal cells resembling those of the cortex. NextĬome a series of Cornu Ammonis areas: first CA4 (which underlies the dentate gyrus), then CA3, thenĪ very small zone called CA2, then CA1. Proper, forming a pointed wedge in some cross-sections, a semicircle in others. Structure, a tightly packed layer of small granule cells wrapped around the end of the hippocampus The first of these, the dentate gyrus (DG), is actually a separate Starting at the dentate gyrus and working inward along the S-curve of the hippocampus means traversing a Schematic diagram showing location of the hippocampus.īasic Hippocampal Circuit File:CajalHippocampus (modified).pngīasic circuit of the hippocampus, shown using a modified drawing by Ramon y Cajal. While most neuroscientists no longer believe in the concept of a unified "limbic system", these regions are highly interconnected and do interact with one another. Paul MacLean once suggested, as part of his triune brain theory, that the limbic structures comprise the neural basis of emotion. These limbic include the hippocampus, cingulate cortex, olfactory cortex, and amygdala.

The structures that line the edge of the hole collectively make up the so-called limbic system (Latin limbus =īorder), with the hippocampus lining the posterior edge of this hole.
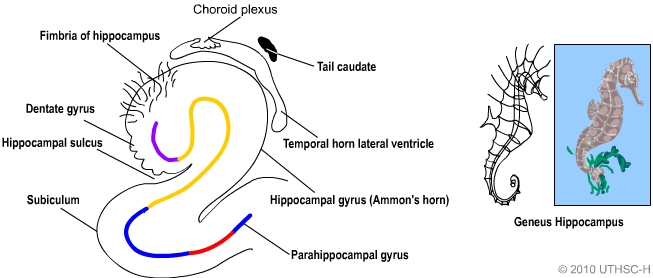
Topologically, one can think of the surface of a cerebral hemisphere as a sphere with an indentation where it attaches to the midbrain. Shape of human hippocampus and associated structures. Due to the three-dimensional curvature of this structure, two-dimensional sections such as are commonly seen in preserved specimens or neuroimaging pictures can show a number of different shapes, depending on the angle and location of the cut. In primate brains, including humans, the portion of the hippocampus near the base of the temporal lobe is much broader than the part at the top. For example, in the rat, the two hippocampi look similar to pair of bananas, joined at the stems. This general layout holds across the full range of mammalian species, from hedgehog to human, although the details vary. It has a distinctive, curved, shape that has been likened to the sea horse monster of Greek mythology and the ram's horns of Amun in Egyptian mythology. The hippocampus is a neural structure in the medial temporal lobe.
Nissl-stained coronal section of the brain of a macaque monkey, showing hippocampus (circled).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
